Perfect Competition
It
is the market structure in which there are large number of buyers and sellers
of a homogeneous product. So, an individual buyer or seller doesn't have market
power. It is extreme case of competitive structure in which each firm has zero
market power i.e. the firm is only price taker.
Features/Assumptions of Perfect Competition
1.
Large number of sellers and buyers
2.
Product homogeneity of every firms
3.
Free entry and exit of firms
4.
Profit maximization is the main objective of all firms
5.
No government regulation
6.
Perfect mobility of factors of production
7.
Perfect knowledge of market among the sellers and buyers
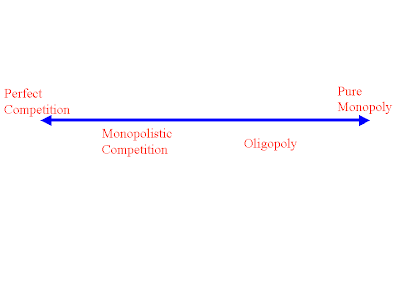
Differences between Perfect Competition and Monopoly
Perfect Competition
- No. of sellers and buyers are very large i.e. infinite. The price of commodity is determined by the market forces of demand and supply and firm is price taker.
- Both AR and MR are represented by a same straight line parallel to output axis. i.e. the demand curve of a firm is perfectly elastic.
- In equilibrium MC=MR=AR
- In equilibrium MC must cut MR by its rising part.
- In long-run, there is normal profit to the firms due to free entry and exit of the firms in the industry.
- The long run equilibrium rests on AR=MR=LAC=LMC=SAC=SMC=P
Monopoly
- Only one firm. The firm behaves as industry and monopolist has right to fix the price level as he leaves the market to determine the quantity of output.
- Both AR and MR fall downward from left to right and AR>MR. The demand curve shows higher the price lower the demand.
- In equilibrium MC=MR and AR>MR
- In equilibrium MC may cut MR by its rising, falling or constant part.
- In long run, there is super normal profit due to strong barrier to entry of new firms.
- The long run equilibrium rests on SMC=LMC=MR
Monopolistic
- No. of sellers and buyers are large but smaller than in perfect competition. The price of commodity is determined by the market forces of demand and supply and firm is price taker. However, the market power is lower than as in monopoly but higher than as in perfect competition.
- Both AR and MR fall downward from left to right and AR>MR. The demand curve shows higher the price lower the demand.
- In equilibrium MC=MR and AR>MR
- In equilibrium MC curve cuts MR curve from below.
- In long-run, there is only normal profit to the firms and no firm can get super normal profit. It's due to free entry of the firms in the industry.
- The long run equilibrium rests on LMC=MR and Price (AR) = LAC but > LMC
No comments:
Post a Comment